SUNFORD VALVES
CV Flow Coefficients
API 6D
| Bore (Inches) | Classes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 300 | 600 | 900 | 1500 | 2500 | |
| 2 | 420 | 420 | 400 | 330 | 330 | 250 |
| 21 / 2 | 690 | 690 | 610 | 520 | 510 | 320 |
| 3 x 2 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 190 | 180 | 200 |
| 3 | 1200 | 1050 | 1000 | 910 | 820 | 500 |
| 4 x 3 | 600 | 600 | 600 | 590 | 550 | 560 |
| 4 | 2200 | 2100 | 1850 | 1800 | 1700 | 1100 |
| 6 x 4 | 800 | 800 | 790 | 790 | 780 | 745 |
| 6 | 5150 | 5100 | 4600 | 4380 | 3800 | 2500 |
| 8 x 6 | 2150 | 2150 | 2150 | 2150 | 2150 | 2150 |
| 8 | 9500 | 9400 | 9000 | 8500 | 7400 | 5300 |
| 10 x 8 | 4300 | 4300 | 4450 | 4450 | 4100 | 4100 |
| 10 | 15000 | 15000 | 14700 | 14500 | 11500 | 8300 |
| 12 x 10 | 7550 | 7550 | 7550 | 8000 | 9000 | 7550 |
| 14 x 10 | 6000 | 6000 | 6000 | 6100 | 6100 | - |
| 12 | 23000 | 23000 | 22500 | 21100 | 18000 | 13000 |
| 14 x 12 | 14000 | 14000 | 14000 | 12800 | 13000 | - |
| 16 x 12 | 9100 | 9100 | 9100 | 8900 | 8900 | - |
| 14 | 28000 | 28000 | 28000 | 25000 | 21000 | - |
| 16 x 14 | 15000 | 15000 | 15000 | 14200 | 14100 | - |
| 16 | 37200 | 37200 | 37200 | 34500 | 27500 | - |
| 18 | 21000 | 21000 | 21000 | 19200 | 19000 | - |
|
Data for Calculation of Flow
The coefficient of flow Cv expresses the rate of flow in gallons per minute at 60°F water with a pressure drop of 1 psig across the valve.The Cv coefficients for the various types and sizes shown in the tables, have been determined from actual flow tests. Note: Kv is the metric equivalent of Cv. KV = CV x 0.85 For Liquids: 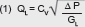 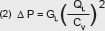 Where QL = Flow in U.S. gallons per minute. Δ P = (P1–P2) Pressure drop in psi. GL = Specific gravity of liquid (water = 1 at 60°F). For Gases: 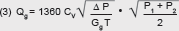 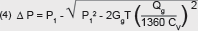 Where Qg = Volumetric flow of gas (SCFH). Gg = Specific gravity of gas at standard conditions. (air at atmosphere and 60°F = 1) T = Absolute temperature of gas (°F + 460). Note: For gas, max. ΔP = 1⁄2 P1, and min. P2 = 1⁄2 P1, and P1, P2 are absolute pressures (psia) |

